Swagger简单使用心得
[TOC]
这里指的是那个在线的 Swagger Editor 网站,不是本地的。在线的用得多舒服呀
为什么要使用 Swagger
在正规的项目开发中,API 接口文档有着极其重要的作用,一份好的 API 文档能大大简化开发的难度,因为 API 文档就是架构设计的体现,良好的架构设计与开发息息相关;同时,一份好的 API 文档还能大大降低沟通成本,节约开发时间。
但是,编写 API 文档本身就是一个相当费事费力的工作,要想编写一份好的 API 文档,不光要有好的文字组织能力,还要有长远的眼光,以及丰富的开发经验。
传统的 API 开发更是如此,书写过程耗费时间,而且开发前期可能需要经常调整接口的访问方式、需要的参数、返回的结果以及文字描述等,容易造成文档更新不及时,进而导致前后端双方沟通成本上升。
现在一些主流的 API 设计工具着重解决的问题就是如何更好地自动化生成 API 文档,大大节约了文档编写时间,并且可以很容易将测试也集成进来。
现在比较好的主流的 API 设计工具主要有两个,分别是 Swagger 和 Postman。这里用 Swagger 是因为之前接触过一些;Postman也挺不错的,更加轻量,可自行了解。
Swagger 是一个规范和完整的框架,用于生成、描述、调用和可视化 RESTful 风格的 Web 服务。
简单说,就是一个兼接口编写、文档编写、交互测试于一身的功能强大的 API 设计/管理 工具,提供了多种编程语言的前后端分离解决方案。
它长这样:
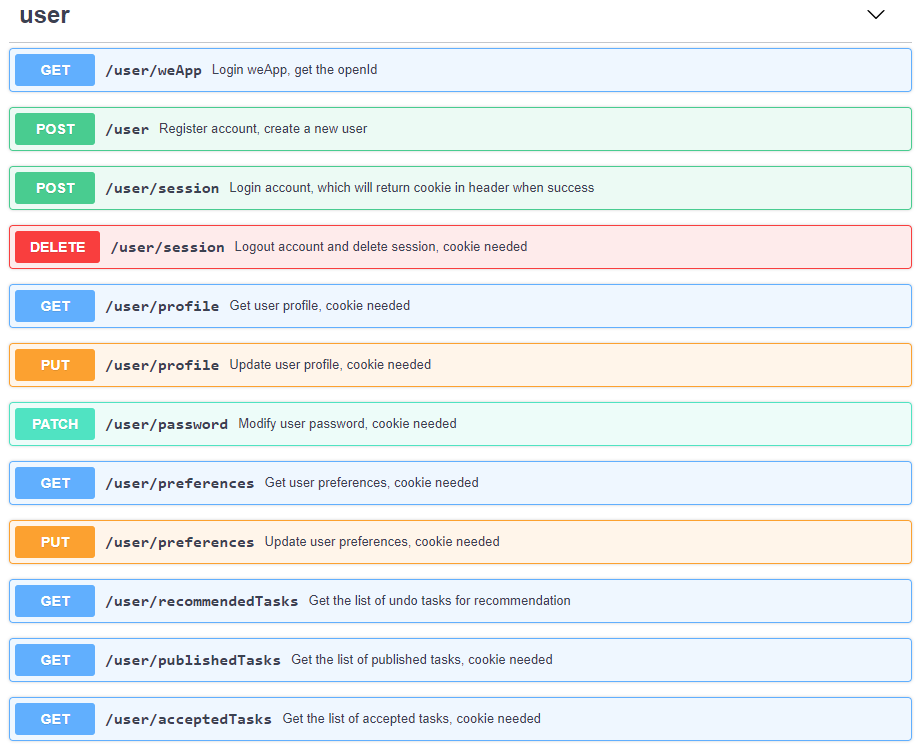
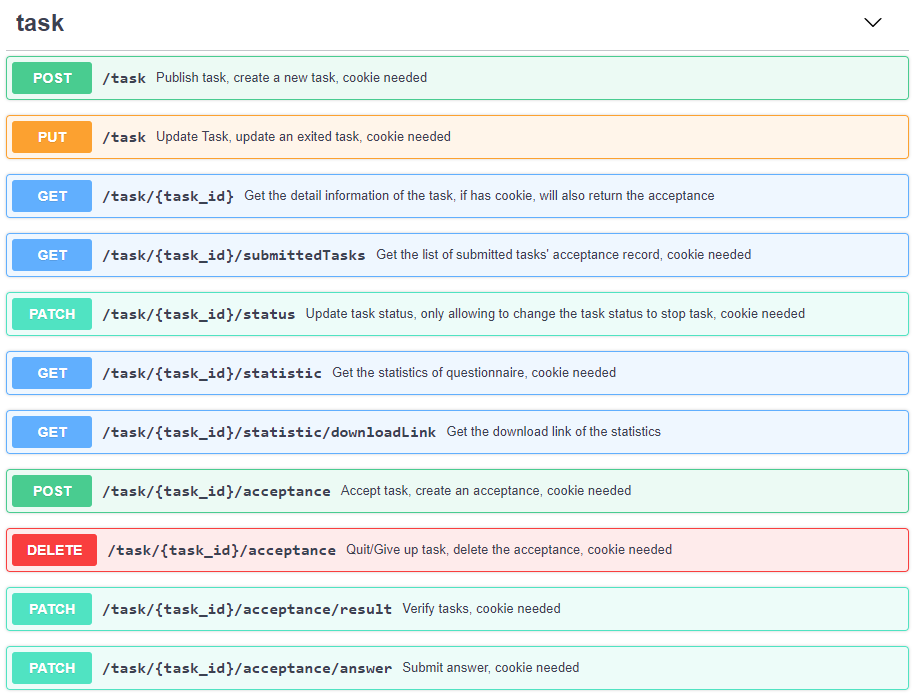
这是我们 包包赚众包平台 项目的部分api,更详细的可以去我们的 API 文档 查看。
一些基本语法
主要就是通过键值对来定义文档,这些键值对都编写在一个 yaml 文件中,在线的 Swagger Editor 可以根据 yaml 自动生成动态可交互的 API 文档。
定义数据结构
一些经常要复用到的数据结构,可以把它们定义成一个组件,在要使用的地方引用即可。当然不定义在语法上也说得过去,但是会增加很多重复的代码,而且修改起来麻烦,改一个地方全都得改。
components:
schemas:
...
task:
type: object
description: Task info
properties:
id:
type: string
description: Task id, which is given after publishing, only can be empty before publishing
publisher_id:
type: string
description: User id of the publisher
name:
type: string
description: Task name
brief_info:
type: string
description: Brief information of the task
type:
type: string
description: Task type, questionnaire is "q", data collection is "d", recruitment is "r"
contact:
type: string
description: Contact of the publisher
requirements:
type: object
description: The types of target people, in json format
tag_id:
type: integer
description: The tag id of the task
ddl:
type: string
description: The deadline for the task
status:
type: integer
description: The status of the task, 0 for "running", 1 for "end", 2 for "stop"
required_count:
type: integer
description: Total count of required tasks
submited_count:
type: integer
description: Total count of submited tasks
finished_count:
type: integer
description: Total count of finished tasks
reward:
type: number
description: Reward for finshing the task (one person)
content:
type: object
description: All content for task, in json format (see schema of task for detail), only used in /task/publishTask api and /task/getTaskDetail api
oneOf:
- $ref: '#/components/schemas/questionnaire'
- $ref: '#/components/schemas/dataCollection'
- $ref: '#/components/schemas/recruitment'
questionnaire:
type: object
description: All content of the questionnaire, in json format
properties:
quest_des:
type: string
description: Descripition for the questionnaire
questions:
type: array
description: All questions
items:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/question'
question:
type: object
description: Each question
properties:
quest_type:
type: string
description: Type of the question
quest_title:
type: string
description: The question
quest_option:
type: array
description: Options of a question
items:
type: string
description: Option
...
type 用来指定数据类型,一般可以是 object,array,string,integer,number等。
description 用来对字段进行描述。
properties 用来指定 object 类型的数据字段有哪些属性。
item 用来指定 array 类型的数据字段的元素类型。
$ref: 'path' 便是上文所说的引用。
oneOf 关键字表示任一都可以,比如上文的 oneOf,就表示 task 的 content 字段的结构可以是 questionnaire,dataCollection, recruitment 三者的结构之一,对应的还有 allOf, anyOf。
定义通用返回头
一些常用的返回头也可以像数据结构那样预先定义好,在需要的地方引用即可。
responses:
200StatusOK:
description: Status OK
content:
application/json:
schema:
type: object
properties:
msg:
type: string
default: 'OK'
400BadRequest:
description: Bad Request
content:
application/json:
schema:
type: object
properties:
msg:
type: string
default: 'Bad Request'
404NotFound:
description: Not Found
content:
application/json:
schema:
type: object
properties:
msg:
type: string
default: 'Not Found'
500ServerErr:
description: Internal Server Error
content:
application/json:
schema:
type: object
properties:
msg:
type: string
default: 'Internal Server Error'
路由
终于到了真正的路由部分。
paths:
...
/user/preferences:
get:
tags:
- user
summary: Get user preferences, cookie needed
responses:
200:
description: OK
content:
application/json:
schema:
type: object
properties:
tag_ids:
type: array
description: All tag ids
items:
type: integer
description: Tag id
400:
$ref: '#/components/responses/400BadRequest'
404:
$ref: '#/components/responses/404NotFound'
500:
$ref: '#/components/responses/500ServerErr'
put:
tags:
- user
summary: Update user preferences, cookie needed
requestBody:
content:
application/x-www-form-urlencoded:
schema:
type: object
properties:
tag_ids:
type: array
description: All tag ids
items:
type: integer
description: Tag id
responses:
200:
$ref: '#/components/responses/200StatusOK'
400:
$ref: '#/components/responses/400BadRequest'
404:
$ref: '#/components/responses/404NotFound'
500:
$ref: '#/components/responses/500ServerErr'
...
/task/{task_id}:
get:
tags:
- task
summary: Get the detail information of the task, if has cookie, will also return the acceptance
parameters:
- name: task_id
in: path
description: Id of the task which is queried
required: true
schema:
type: string
responses:
200:
description: OK
content:
application/json:
schema:
type: object
properties:
task:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/task'
acceptance:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/acceptance'
400:
$ref: '#/components/responses/400BadRequest'
404:
$ref: '#/components/responses/404NotFound'
500:
$ref: '#/components/responses/500ServerErr'
...
首先需要注意的是路由是唯一的,一个路由如果有多个方法,应该把多个方法都写在同一路由下,而不是拆开多个路由。
get、put、post等指的是请求类型。
tags 可以给路由打标签,实现路由分组。
summary 描述这个路由的作用,相当于路由的 description。
parameters 可以指定显式的路由参数。
in字段指定参数形式。query表示参数出现在 get 方法 url 中的 ? 后面。path或者出现在路径里的参数。
name是参数名字。required表示参数是否必须。schema指定参数格式。
requestBody 可以指定隐式的路由参数,这些参数都在请求体中。
content下面的application/json或application/x-www-form-urlencoded是用来指定请求体的格式。schema指定参数格式。
responses 指定返回结果的格式。
200、400、404、500等指定返回的状态码。content下面的application/json或application/x-www-form-urlencoded是用来指定返回体的格式。